PRE-RELEASE
Brief description
| Brief description |
| - |
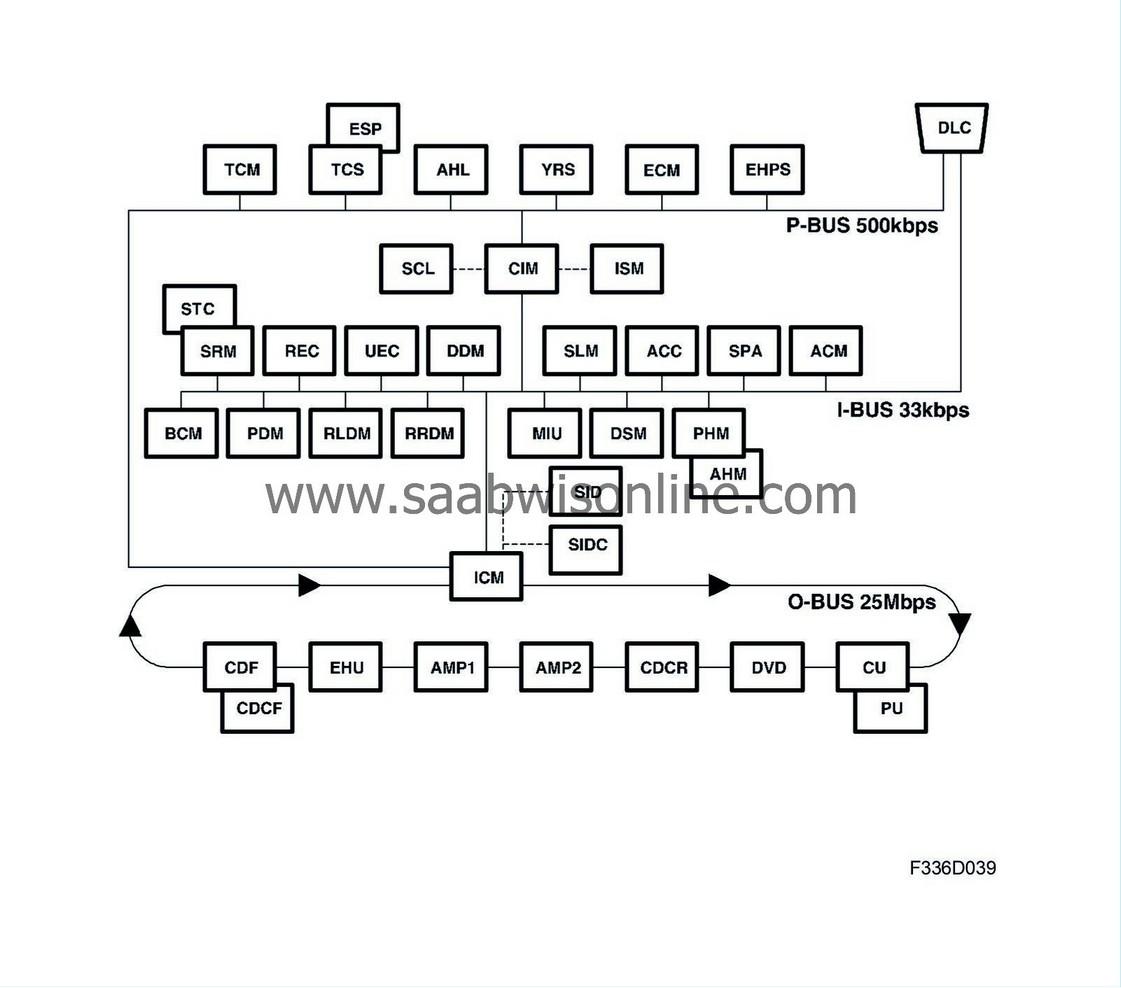
P-bus (Powertrain bus)
|
|
| - |
I-bus (Instrument bus)
|
|
| - |
O-bus (Optical bus).
|
|
A control module sends a message by sending ones and zeros in a predefined order. The control module only sends a message if no other control module is presently sending. The meaning of the combinations of ones and zeros is predefined so that all the control modules can interpret the information in the same way. The message contains information about what is being sent and the value, for example ”Coolant temperature" 100°C or ”A/C ON".
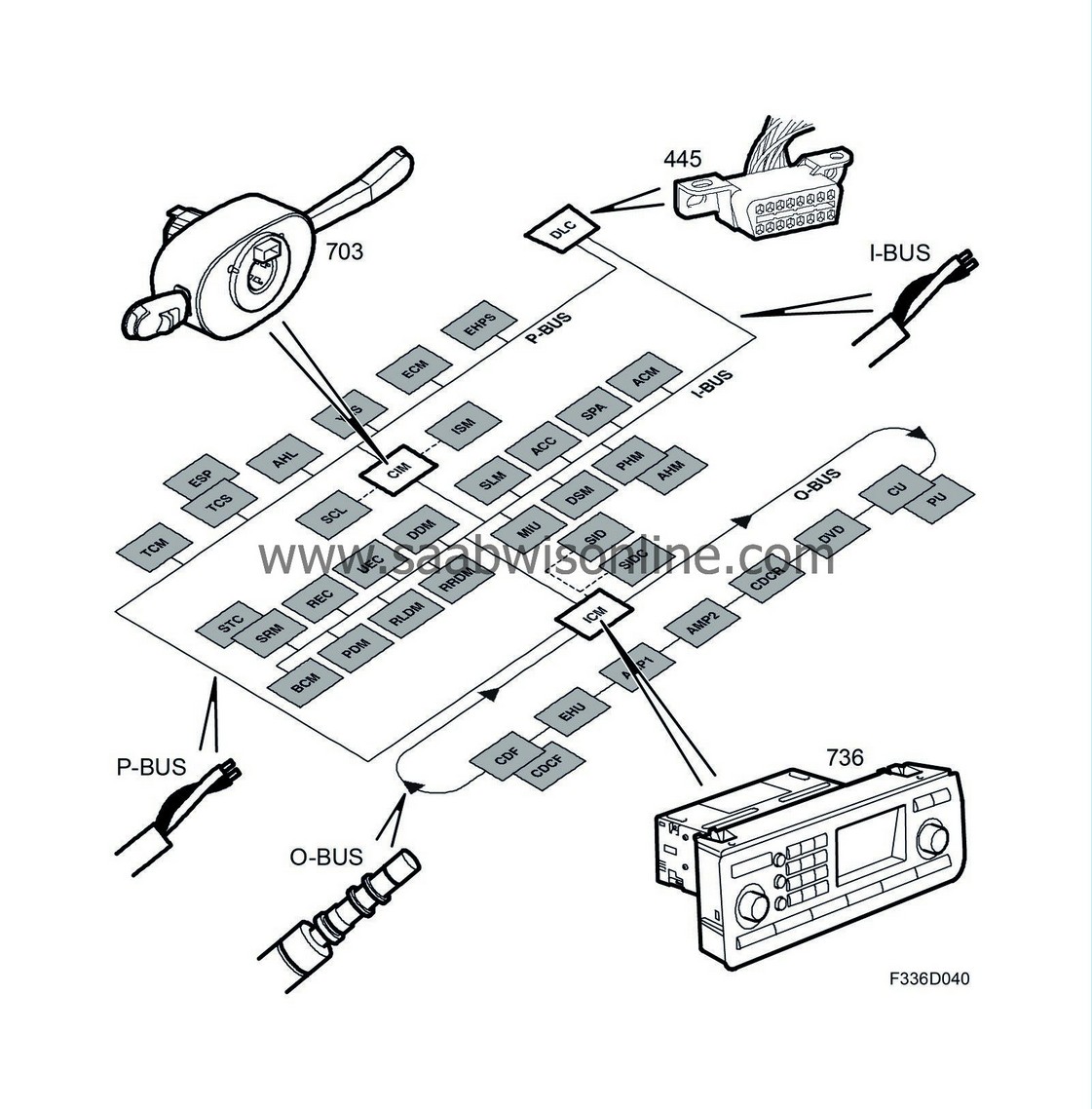
The data link connector can access both the P-bus and the I-bus. With an adapter, Tech2 can be connected to the data link connector and can communicate with the different control modules on the P-bus and I-bus. Diagnostic communication with the control modules on the O-bus occurs via the ICM, which functions as a "gateway".
Certain information sent by a control module is made available to all other bus control modules. The CIM relays information between the I-bus and P-bus. The ICM makes sure that information available on the I-bus and P-bus is available on the O-bus, and vice versa.
| P-bus and I-bus |
The P-bus and I-bus are connected to the CIM and ICM. The buses are electrically isolated. The P-bus has a data transfer rate of 500 kbits/s and the I-bus of 33 kbits/s. The data rate on the P-bus is high to allow the powertrain systems access to information with the shortest possible delay, for example during air mass compensation when the selector lever is moved from N to D or torque limitation during gear changes.
Information on the P-bus is transferred between control modules on two leads: bus + (green lead) and bus - (white lead). The leads are twisted to reduce their sensitivity against electrical interference. The I-bus only has one lead.
| O-bus |
The O-bus differs from the P-bus and I-bus in that it is an optical ring bus. Two optical fibres are connected to each control module on the bus; one fibre for incoming data and one for outgoing data. Received messages are converted by each control module from optical signals into electrical signals and then back again into optical signals. The O-bus has a data transfer rate of 25 Mbit/s
In the most basic model of the car, there are only optical cables behind the dashboard between the ICM and EHU. In other car variants, the optical cables are routed to the luggage compartment, which can contain other units.